Sexanda Explained
Saxenda (Liraglutide) is a prescription medication specifically designed to aid in weight loss and maintenance. It functions by mimicking the action of a hormone called GLP-1 that targets areas of the brain regulating appetite and food intake. By enhancing feelings of fullness and reducing hunger, Saxenda helps individuals consume fewer calories and lose weight.
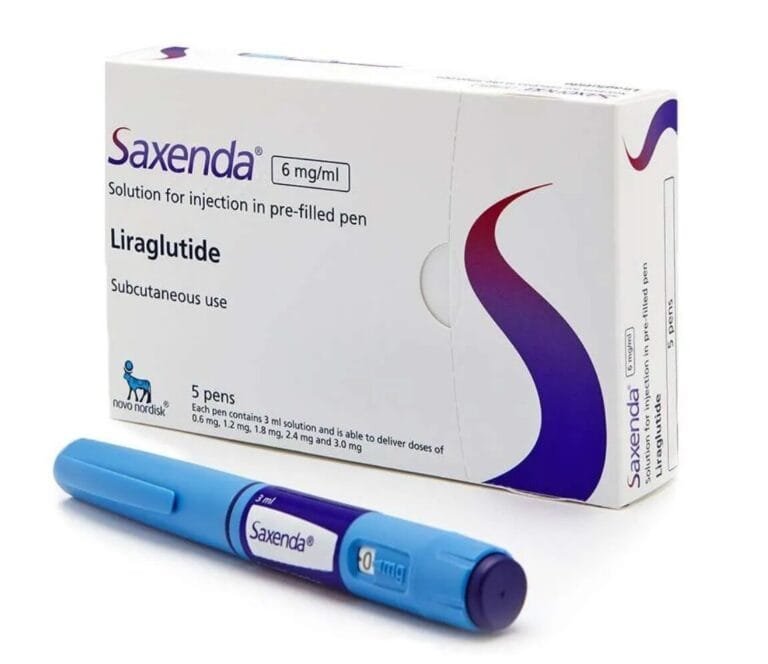
Saxenda Eligibility
Saxenda is intended for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher (obesity) or those with a BMI of 27 or higher (overweight) who also have weight-related health conditions. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your overall health, weight loss goals, and any underlying conditions to determine if Saxenda is a suitable option for you
How to use Saxenda
Saxenda is prescribed by a healthcare provider and is administered as a subcutaneous injection. The typical dosing schedule starts with a lower dose, which is gradually increased over several weeks to the full dose to help minimise side effects and allow your body to adjust. For this reason, Saxenda is available as an initial pack and a maintenance pack.
Initial Pack
Each Saxenda pre-filled pen contains enough for 17 days’ worth of doses. A full pack contains 5 pre-filled pens which are enough for 6 weeks’ worth of treatment. Unlike other weight loss injections, Saxenda needs to be injected once daily.
Your dose of Saxenda will be increased in intervals of 0.6mg, up until a maintenance dose of 3mg is reached
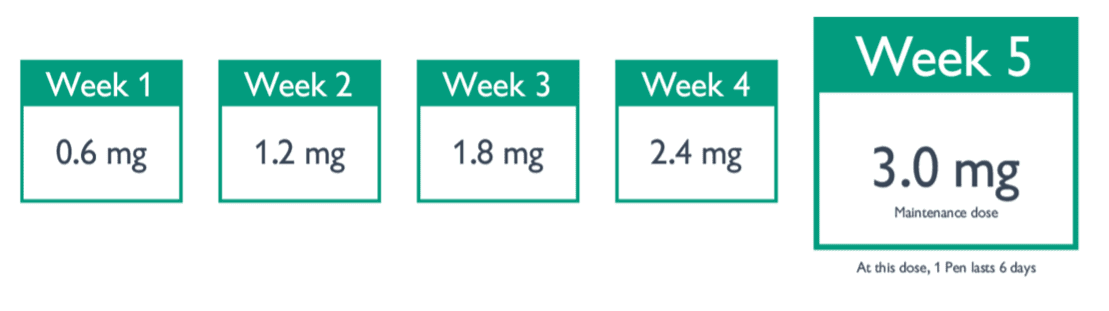
Maintenance Pack
Once the maintenance dose is reached, each daily injection from then on would be 3mg. Therefore one pre-filled pen lasts 6 days.
Side effects of Saxenda
The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation, and low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). These symptoms are usually mild to moderate and tend to diminish as your body gets used to the medication.
Reducing Side effects
- Gradual dose increase
- Drink plenty of fluids to manage nausea and prevent dehydration
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to manage gastric symptoms
- Avoid high-fat and high-sugar foods
Saxenda and the Birth Control Pill
Saxenda can reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills. Patients using oral contraceptives should also use an additional barrier method, such as a condom, to prevent pregnancy.
Ready to start a consulation?
Benefits of Using Us
We offer a 360° weight loss plan with a focus on diet, exercise, and clinical methods.
Holistic approach with diet and exercise support.
Digital/in-person* support available.
Same day consultation process.
Our programme is managed by

